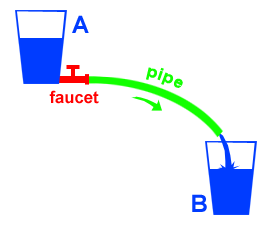
In principle, the basic electrical circuit consists of three parts:
- Voltage source: Voltage source (Power Supply) can be either voltage AC (Alternate Current) 220-240 VAC from the power company or a DC voltage (Direct Current) like an Accumulator (Battery Cell)
- Conductor: Conductor can be a cooper wire, cable, or other objects that are conductive.
- Load: Load can be either electric or electronic devices such as televisions, refrigerators, washing machines, computers, electric motors, radios, lamps, LEDs, etc.

If the resistance of the conductor ignored or considered to be zero (0 Ohm). The greater voltage source, the greater current flowing to the load. The larger the load resistance, the smaller current flowing in the electrical circuit. In this condition shall apply Ohm's Law.
Ohm's law is a statement that the electrical current flowing through a conductor is always proportional to the applied potential difference to it. A conductive object will be in accordance with Ohm's law if the resistance value does not depend on the value and polarity of the potential difference. Although this statement does not necessarily apply to all types of conductors, but the term "law" still used by historical reasons.
Mathematically Ohm's law written by the equation:

"I" is electric current flowing in a conductor in Amperes (A), "V" is the voltage present at both ends of the conductor in Volts (V), and "R" is the resistance contained in a conductor in Ohm . This law was initiated by George Simon Ohm, a physicist from Germany in 1825 and published in a paper titled The Galvanic Circuit Investigated Mathematically in 1827. (Wikipedia)